In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled Ninetails, a novel computational tool designed to analyze the intricate composition of poly(A) tails present in messenger RNA (mRNA). This development holds significant implications for understanding how these integral RNA components influence genetic stability and translation, particularly in the context of therapeutic mRNAs, such as those used in COVID-19 vaccines.
Poly(A) tails are vital for the stability and function of eukaryotic mRNAs, acting as crucial regulators of mRNA export, translation initiation, and degradation. Traditionally viewed as simple stretches of adenosine nucleotides, recent findings have unveiled a more complex picture. Studies suggest that non-adenosine nucleotide decorations are more common than previously believed, significantly affecting mRNA's cellular behavior.
Developed using advanced neural network techniques, Ninetails distinguishes itself from existing methods by accurately identifying and quantifying non-adenosines within poly(A) tails without the biases introduced by amplification processes in earlier sequencing technologies. These advancements are made possible through direct RNA sequencing (DRS), which allows for the characterization of native RNA molecules and provides insights into the natural composition of poly(A) tails.
The research team applied Ninetails in various biological contexts and discovered that the prevalence of non-adenosines varies significantly based on several factors, including the type of mRNA, the originating cell type, and even species. Notably, substrates of cytoplasmic TENT5-polymerases and mitochondrially encoded mRNAs exhibited a heightened frequency of these non-adenosine decorations.
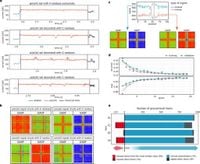
In examining therapeutic mRNAs specifically, the study revealed that the composition of poly(A) tails in mRNA vaccines, such as the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine, changes throughout its cellular lifetime. This dynamic behavior suggests that the manufacturing protocols of synthetic mRNAs can impact their characteristics and overall effectiveness in therapeutic applications.
During the analysis, the researchers found that in macrophages, which are the primary target cells for mRNA-1273 post-administration, the poly(A) tail underwent observable changes that enhance its stability and efficacy. For example, after 24 hours of treatment, the length of the poly(A) tails in the target cells extended significantly, revealing a complex interplay between mRNA and its cellular environment.
Previous methods for investigating poly(A) fabrications often suffered from significant limitations, primarily due to the amplification process that distorted the true representation of nucleotide composition. Ninetails circumvents these issues and presents a more reliable framework for subsequent biological studies, potentially paving the way for optimized mRNA therapeutics.
According to the researchers, "Our work provides an efficient, high-throughput, and reproducible framework for the detection and quantification of non-adenosines in poly(A) tails." This statement encapsulates the promise of Ninetails, not only to advance the scientific understanding of mRNA variations but also to enhance the development of future mRNA vaccines.
The study's findings highlight that the non-adenosine content can greatly affect the stability and functionality of mRNAs, suggesting a need for further exploration into how these modifications influence mRNA behavior in vivo. This knowledge is critical as the field of mRNA therapeutics continues to expand, especially amid the backdrop of a global pandemic that has propelled mRNA technology to the forefront of vaccination strategies.
As researchers continue to dissect the complexities of mRNA and its interactions within biological systems, tools like Ninetails represent a great leap forward in understanding how to enhance mRNA vaccines and other therapeutic applications. With the ever-increasing pace of innovation in this field, the implications for public health and treatment efficacy remain profound, marking a significant step towards more effective future mRNA therapeutics.
In conclusion, the introduction of Ninetails represents a promising advancement in RNA analysis, reaffirming the importance of comprehensively understanding poly(A) tail dynamics as essential not only for genetic regulation but also for the development of reliable therapeutic interventions.