In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers have made significant strides in improving breast cancer treatment using pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, known as Doxil, in conjunction with the antiemetic aprepitant. The study reveals that this combination therapy not only enhances the antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin but also reduces adverse side effects traditionally associated with chemotherapy.
Breast cancer remains a global health crisis, having claimed the lives of approximately 670,000 individuals in 2022 alone, according to the World Health Organization. As one of the most common malignancies affecting women, the disease is known for its heterogeneity and complex treatment challenges. Traditional chemotherapy, particularly with doxorubicin, can lead to severe side effects, including cardiotoxicity, which complicates treatment regimens.
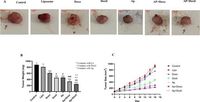
To address these concerns, the researchers cleverly formulated doxorubicin in liposomes—specifically, pegylated liposomes designed to improve drug delivery while minimizing toxicity. Their investigation utilized a mouse model implanted with 4T1 breast cancer cells, allowing for a direct comparison between the efficacy and safety profiles of Doxil and conventional doxorubicin.
The findings indicated a remarkable improvement in tumor size and weight in the groups treated with Doxil compared to those receiving standard doxorubicin. Furthermore, the combination of Doxil and aprepitant produced synergistic effects, further curtailing tumor growth. Notably, mice that received Doxil exhibited significantly reduced oxidative stress markers in both cardiac and liver tissues, which are known for being vulnerable to the toxic effects of chemotherapy.
As highlighted in the study, treatment with Doxil resulted in a significant increase in oxidative stress, evidenced by elevated malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. In stark contrast, aprepitant demonstrated potent antioxidant properties, effectively lowering MDA levels and enhancing the activity of key antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT).
The detailed histopathological assessment revealed that the liposomal formulation increased necrosis within tumor tissues, suggesting a more effective treatment outcome. Moreover, the study noted that aprepitant appears to alleviate the cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin, preserving cardiac tissue integrity more effectively than the standard treatment alone.
The researchers further elaborated on the rationale for using aprepitant—an FDA-approved drug primarily aimed at preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Aprepitant functions by blocking the neurokinin-1 receptor, which, when activated by substance P, exacerbates chemotherapy-related side effects. Thus, the combination of Doxil with aprepitant not only enhances antitumor efficacy but also paves a pathway towards safer cancer treatment options.
These results signify a pivotal advancement in breast cancer therapy, providing insights into how nanotechnology and combination therapy can enhance treatment effectiveness while mitigating unwanted side effects. By tackling both the efficacy and toxicity profiles of existing treatments, researchers are steering the future of chemotherapy towards more personalized and effective approaches.
As the study concludes, further investigations are warranted to fully assess the long-term safety and effectiveness of this innovative treatment modality in clinical settings. The ongoing exploration of liposomal formulations combined with existing therapies could usher in a new era in breast cancer management, offering hope to millions facing this formidable disease.