In recent years, the increasing demand for ecosystem services has come under threat due to the rapid urbanization seen in many regions. A recent study published in Scientific Reports sheds light on this pressing issue, specifically focusing on the carbon sequestration capabilities of terrestrial ecosystems in Pingshan County, Hebei Province, China, from 2000 to 2022.
This research, conducted against the backdrop of China's dual carbon goals aimed at achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality, investigates the intricate relationship between land-use change and ecosystem service degradation. The study utilizes land-use data processed through the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs (InVEST) model's Carbon module to assess changes in carbon stock over the two-decade span.
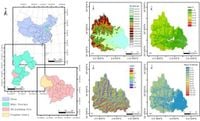
According to the researchers, Pingshan County presents a unique ecological environment with significant geological variations shaped by its topography, including elevation, slope, and aspect. This heterogeneity proves crucial in understanding the dynamics of carbon sequestration. "The geological environment exerts the most significant influence on carbon stock, followed by land-use types, while geological disasters have the least impact," wrote the authors of the article.
The findings from this study reveal a consistent increase in carbon stock across Pingshan County over the past two decades, fueled by an increase in forest and cultivated land, which now represents 94.76% of the county's total area. The county, with its warm temperate semi-humid climate characterized by an average temperature of 12.7°C, has been undergoing significant land-use changes due to both urbanization and the implementation of ecological policies.
The impact of geological features is notable, with areas of elevation ranging from 310 to 910 meters demonstrating the highest average carbon stock, exceeding 105 tons. Conversely, regions above 1710 meters show lower carbon stocks due to harsher climatic conditions and less favorable vegetation growth. The researchers observed, "The protection and enhancement of carbon storage in Pingshan County are of great significance for the sustainable development of the regional ecological environment," underscoring the necessity of incorporating geological considerations into future conservation strategies.
A key observation made by the research team is the decline in grassland areas, attributed to rapid urbanization and the expansion of construction land, which has increased by 51.85 km² since 2000. This shift led to a decrease in the quality and quantity of ecosystem services provided by these natural landscapes. Adjustments in land-use policies, particularly in the context of ecological civilization construction, are essential to maintaining biodiversity and ecological health.
Examining the influence of geological disasters, such as landslides, the study notes that while these events can damage vegetation, Pingshan County's ecological resilience is largely supported by its healthy forests and grasslands. Notably, geological hazards predominately occur in the 210 to 910 meters elevation range, which constituted 70.70% of total disaster occurrences. The study suggests that enhancing vegetation areas can bolster carbon sequestration capabilities, thereby contributing to overall ecological stability.
As Pingshan County continues to modernize and implement ambitious ecological policies, the research emphasizes a proactive approach to land use planning. Future strategies should involve strengthening the protection of existing forests and cultivated lands while promoting sustainable agricultural practices that align with the dual carbon targets. The predominance of forest land in areas with suitable climatic and geological conditions indicates the potential for optimizing land use to maximize carbon sequestration.
This study serves as an essential foundation for subsequent ecological and environmental research, paving the way for future studies that will further illuminate the diverse factors driving changes in carbon stock. By detailing the implications of geological, environmental, and policy-related factors, this comprehensive analysis will guide significant actions towards ecological conservation and sustainable development.