A recent study published in Scientific Reports reveals significant changes in vegetation dynamics across the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2015, focusing on how these changes respond to climate factors.
The research utilized a high-resolution Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) dataset, showing that 86% of the area exhibits a greening trend, while 14% reflects browning.
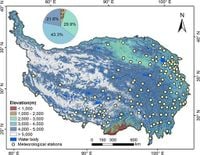
The most pronounced greening occurs at elevations below 1,000 meters, with a notable gradient distribution upwards, indicating that the lower altitudes are benefitting most from climatic changes.
An analysis of breakpoints in NDVI trends during this period highlighted a sharp shift around 1998, with 70.1% of the vegetation experiencing abrupt changes.
The authors found that temperature significantly influences NDVI dynamics compared to precipitation, suggesting a need for adaptive management in response to climate change in ecologically sensitive areas.
The research is critical in understanding the impacts of climate change on ecosystems in vulnerable regions, particularly how elevation modifies these influences and the relationships between various climatic elements.
The findings promote an approach for future research which includes enhanced ecological monitoring and the incorporation of additional climatic variables.
Overall, the study lays the groundwork for ongoing efforts aimed at understanding vegetation responses to climate change at high altitudes.