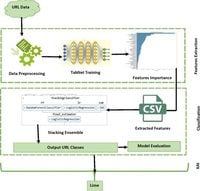
The rise of internet technologies has led to increasing concerns surrounding cybersecurity, particularly the identification of malicious URLs that can expose users to various threats like phishing and malware. A recent study has unveiled a promising new tool in this ongoing battle: the Robust unified TabNet ensemble model, designed specifically to tackle the issue of malicious URL identification effectively.
Developed by a team of researchers led by M. Naseer and F. Ullah from the University of Bisha, this innovative model employs a fine-tuned attention-based deep neural network called TabNet to extract key features from URLs, enhancing classification accuracy significantly. With an outstanding accuracy of 97.8%, precision of 0.978, recall of 0.976, and F1-score of 0.978, the model stands out as one of the most effective systems developed to date for URL classification.
One of the key motivations driving this research is the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Traditional detection methods, including signature-based and rule-based systems, have proven inadequate in the face of ever-evolving malicious tactics. The authors of the article emphasize, "With an accuracy of 97.8% and F1-score of 0.978, our model shows a significant improvement in identifying malicious URLs." This highlights the urgent need for more dynamic solutions in cyber defense.
The methodology behind the TabNet ensemble model is centered around machine learning (ML) techniques, particularly those reflecting a stacking ensemble approach. This involves the integration of multiple learning algorithms to improve the overall performance of the model. The authors collected data from a range of sources, including more than 35,300 benign URLs from Alexa's top websites, 12,000 spam URLs from the WEBSPAM-UK2007 dataset, and nearly 10,000 phishing URLs from the OpenPhish repository.
To ensure robust validation, the research measured metrics like accuracy and employed Kappa statistical analysis to assess model performance effectively. The Kappa statistic value for the proposed model indicates a high level of agreement between true and predicted values, demonstrating the model's efficacy in identifying obfuscated URLs—important as they are often used by malicious entities to deceive unsuspecting users. The authors state, "The Kappa statistic value for the proposed model indicates a high level of agreement between true and predicted values, demonstrating the model’s efficacy."
During the experimentations, the researchers utilized a 10-fold cross-validation approach, yielding a mean accuracy of 97.27% with a narrow confidence interval of 0.004. These results affirm not only the robustness of the model but also its potential scalability and applicability across a range of real-world scenarios.
Furthermore, the model leverages an explainable AI (XAI) technique known as Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME). This method serves to illuminate the decision-making processes behind the model, increasing transparency and fostering user trust in machine learning solutions. Achieving a consensus on feature contributions is crucial for regulatory compliance and establishing credibility in AI-based systems.
As the research concludes, the authors suggest that future studies focus on enhancing the model's performance through additional data sources, particularly those incorporating various examples of obfuscated URLs from different environments. They also propose exploring the implementation of the model on edge devices to ensure functionality in areas with limited computational resources.
This study represents a significant stride in combating the threats posed by malicious URLs, contributing valuable insights to both the academic community and cybersecurity practitioners. As cyber threats continue to evolve, innovations like the TabNet ensemble model will play an essential role in ensuring safer online experiences for all users around the globe.