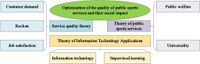
In an effort to enhance the quality of public sports services, a recent study has analyzed related data using a supervised learning model. This innovative approach revealed significant findings that could reshape how public sports services are optimized and delivered.
The study, which achieved an impressive accuracy rate exceeding 88%, indicates that implementing this model not only improves service quality but also meets the diverse needs of the public more effectively. By addressing key factors influencing service delivery, the research lays a solid foundation for future policy and strategic decision-making in public sports offerings.
According to the authors of the study, the research aims to respond to the increasing demand for improved public sports services as society evolves. They stated that, "With the swift progress of information technology, particularly artificial intelligence and big data, new ideas are now available for optimizing public sports services." This underscores the potential of technology to meet growing expectations for sports facilities and services.
The research suggests that by systematically collecting and analyzing data on service processes, facility conditions, and personnel management, authorities can better identify weak links in service delivery. The authors note, "A comprehensive evaluation framework is established, which can accurately identify key factors affecting service quality." This evaluation framework serves as a groundbreaking method for enhancing user experiences and overall public satisfaction.
In practical terms, the use of the supervised learning model enables sports administrators to predict future service demands while optimizing resource allocation. This is particularly vital given the increased user engagement and expectations surrounding public sports facilities. Past studies, such as those by Bunker et al. in 2021, have demonstrated the model's ability to forecast service demands effectively.
Furthermore, recent evaluations utilizing datasets from platforms like Weibo have provided astonishing results: a model accuracy of 91% coupled with a recall rate exceeding 90%. This signifies that not only can the model effectively process public sports service data, but it also identifies key areas for improvement. As the study articulates, "The model exhibits remarkable advantages and potential in optimizing public sports service quality, affording robust support for service enhancement initiatives."
This comprehensive analysis comes at a crucial time when public health and fitness have taken center stage in societal discourse. The findings emphasize the role that well-structured public sports services play in promoting public engagement in physical activity and enhancing overall health outcomes.
Moreover, through targeted optimization strategies proposed by the study, such as enhancing facility conditions, refining service processes, and improving personnel quality, sports services can better align with user expectations. Researchers advocate for the necessity of adopting innovative approaches, such as integrating supervised learning models with other advanced technologies like cloud computing, to elevate the service quality.
Ensuring that these models evolve and adapt to emerging trends will be essential for sustaining improved public sports services. The authors conclude by stating, "Future research will persist in refining model performance and broadening application scopes, contributing more wisdom and strength to the improvement of public sports service quality."
In summary, this research not only contributes new insights into optimizing public sports service quality but also acts as a catalyst for enhancing public health through increased participation in sports. As public sports offerings continue to evolve alongside societal demands, the implications of this study are poised to significantly affect the future of public health and sports administration.