In a groundbreaking study, researchers have developed an advanced method for extracting bioactive compounds from Liquorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra) using a combined ultrasonic and cold plasma approach, significantly enhancing extraction efficiency compared to traditional methods.
Liquorice root has been valued for its medicinal and sweetening properties for centuries. Recent findings highlight the effectiveness of a technology that combines ultrasonic extraction with cold plasma treatment, revealing substantial improvements in the yield and quality of bioactive compounds.
The study, published on March 22, 2025, aimed to address the limitations of conventional extraction methods, which often involve lengthy procedures, high solvent usage, and energy consumption. By integrating ultrasonic and cold plasma techniques, the researchers achieved higher extraction yields and improved compound quality, establishing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly method.
Researchers evaluated the new method through a set of carefully controlled experiments utilizing Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Box-Behnken design, optimizing extraction variables like ultrasonic power, extraction time, and argon-to-air ratio in the cold plasma system.
Results revealed marked increases in the concentration of total phenolics, flavonoids, and glycyrrhizic acid—key bioactive components linked to numerous health benefits. Specifically, total phenolic content increased by 10.23%, 15.96%, and 13.29% for the ultrasonic, cold plasma, and combined methods, respectively, compared to traditional maceration techniques.
Furthermore, the total flavonoid content showed impressive rises of 21.47%, 22.19%, and 42.41%, and glycyrrhizic acid content climbed by 10.84%, 12.38%, and 15.89%, which highlights the superior effectiveness of the integrated approach.
The team behind the study consisted of acclaimed researchers from Shahrekord University, who emphasize the significance of their findings in advancing extraction technologies. "The combined ultrasonic-cold plasma technique exhibits a remarkable synergy," the authors of the article stated, underscoring the method's potential for commercial applications.
In addition to increasing yield and concentration of bioactive compounds, this method also adheres to green extraction principles, prioritizing the use of less energy and safer solvents. It stands in contrast to traditional extraction methods, which have been criticized for their environmental impact.
According to the experimental data, prolonged extraction times contributed positively to the total phenolic and flavonoid content, although maximal improvements were noted at strategic timeframes. Optimal conditions determined through this research suggest a balance between extraction duration and technological parameters is crucial to maximally extract these beneficial components.
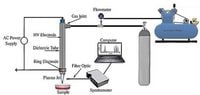
The researchers utilized various methods—including cold plasma extraction with a dielectric barrier discharge and ultrasonic-assisted extraction—to enhance the release of bioactive compounds from the plant materials effectively.
Specifically, ultrasonic extraction employed cavitation, which disrupts cellular structures, facilitating higher yields. Meanwhile, cold plasma treatment chemically modifies plant cell walls, allowing better solvent penetration and enhanced compound release.
The comparative performance of the extraction methods was rigorously assessed. The results indicated significant increases in yields produced with the ultrasonic-cold plasma method versus conventional maceration and single extraction techniques. In total, the new approach yielded 118.64 mg/g of glycyrrhizic acid—the highest concentration reported in this study.
Research indicates the antioxidant capacity of Liquorice extracts is an essential component of its therapeutic properties, and this combined extraction method successfully emphasizes that aspect by demonstrating reductions in the IC50 value, which indicates increased antioxidant activity.
This study ultimately marks a significant step toward refining extraction methodologies in the food and pharmaceutical industries, paving the way for more effective and eco-conscious extraction processes. By improving extraction yield and compound integrity while adhering to environmental standards, this pioneering technique holds promise for large-scale applications in the future.
Conclusively, while this research offers substantial advancements, further optimization and assessment of economic viability and environmental impact in commercial settings remain key areas for future investigation. Such efforts will be crucial for integrating this novel extraction technique into broader industrial practices.