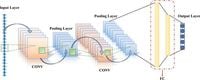
In the pursuit of more effective and efficient diagnostic techniques for machinery, especially rolling bearings, researchers are unveiling a hybrid method that combines advanced machine learning with optimization algorithms. This innovative approach leverages the capabilities of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and bidirectional long short-term memory networks (BiLSTMs) enhanced by a hybrid Grey Wolf Algorithm (HGWA) to achieve remarkable accuracy in bearing fault diagnosis, even under challenging conditions.
Bearings, integral to a multitude of mechanical systems, are often subjected to harsh operational environments that lead to wear and damage. Identifying failing components in these systems is vital for maintaining operational safety and efficiency. Conventional methods of fault diagnosis rely heavily on large datasets to train models, which can be a significant drawback, particularly when data is scarce or imbalanced.
The proposed hybrid model not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also improves the optimization process. According to the study, the model achieved 100% diagnostic accuracy across various operating conditions using the Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) dataset. This level of performance was attained even when only a limited number of training samples were available, indicating strong generalization capabilities.
At the heart of this advanced system is the integration of CNNs for spatial feature extraction alongside BiLSTMs that capture temporal dependencies crucial for time-series data. The HGWA optimizes the hyperparameters of the model, minimizing the manual effort typically required in model tuning and allowing for quicker adaptations in different environments.
Research indicates that deep learning, particularly CNNs, has become increasingly prominent in machinery fault diagnosis. Previous work has led to models utilizing diverse techniques to improve detection, yet the integration of HGWA is groundbreaking, promoting faster convergence and avoiding local optima commonly encountered in other optimization methods.
"The ability to fine-tune a pre-trained model using a small training dataset significantly enhances the performance of fault diagnosis systems," noted the authors. This aspect is particularly important in real-world applications where obtaining extensive labeled datasets is often impractical. The findings reveal that the model can effectively capture high-dimensional features from raw acceleration signals, facilitating precise identification of fault types.
The implications of this research are profound. Not only does it pave the way for the adoption of hybrid models in diagnostics, but it also opens avenues for future investigations into other types of machinery failures beyond rolling bearings, including applications in industries such as energy, transportation, and manufacturing.
Future research will likely revolve around refining the model further, focusing on real-time performance and computational efficiency while exploring its potential in varying industrial contexts. As technology continues to evolve, the combination of deep learning and intelligent optimization algorithms will enhance the reliability and effectiveness of fault diagnosis systems, ensuring safer and more efficient machinery operation across diverse environments.
The study strongly highlights the importance of developing more adaptive diagnostic models that are not only accurate but also resource-efficient, setting a new standard in the field of predictive maintenance for industrial applications.