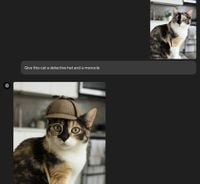
OpenAI has recently introduced a powerful upgrade to its ChatGPT platform, allowing users to create and modify images in the iconic style of Studio Ghibli. This innovative feature has proven so popular that the company has been forced to impose temporary restrictions on its use. The announcement, made on March 25, 2025, has ignited a wave of excitement among users, prompting them to transform everything from personal photos to popular memes into Ghibli-style artwork.
CEO Sam Altman noted the overwhelming response, stating, "It's really fun to see that people love the images on ChatGPT, but our GPUs are melting." This comment highlights the intense demand for the new feature, which has led to concerns about the sustainability of OpenAI's infrastructure. As users flock to the platform to create Ghibli-inspired images, the company's servers are feeling the strain, prompting the need for a temporary cap on usage.
The new image generation capability, powered by the advanced GPT-4o model, allows users not only to create images but also to edit existing ones. This functionality is available through a $200-per-month subscription to the Pro plan, with plans to roll it out to Plus and free users in the near future. The upgrade marks a significant leap forward for OpenAI, as it aims to compete with other AI models, including xAI, developed by Chinese competitors.
However, the introduction of this feature has raised serious ethical questions regarding copyright infringement. OpenAI has faced scrutiny for training its AI on copyrighted material, including works by Studio Ghibli founder Hayao Miyazaki. In a technical document released alongside the update, the company stated it would adopt a "conservative approach" to mimicking the aesthetics of individual artists. Notably, OpenAI has implemented a rejection mechanism that prevents users from generating images in the style of living artists.
Despite these measures, the legality of using Studio Ghibli's work remains a contentious issue. As Altman pointed out, the company is already embroiled in copyright battles with several American newspapers for using their content to train ChatGPT. This ongoing legal landscape raises the question: "Does the company have a license to use Studio Ghibli's work?"
Since the release of the image generator, social media platforms have been flooded with AI-generated images depicting Studio Ghibli versions of various subjects, including notable figures like Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump. Memes featuring these transformed images have gone viral, demonstrating the feature's potential for creativity and humor. However, the rapid spread of these creations has also drawn attention to the potential for misuse and the ethical implications of AI-generated art.
OpenAI's chief operating officer, Brad Lightcap, emphasized the company's commitment to respecting artists' rights, stating, "We’re respecting of the artists’ rights in terms of how we do the output, and we have policies in place that prevent us from generating images that directly mimic any living artists’ work." This assertion aims to reassure both artists and the public that OpenAI is taking the issue of copyright seriously.
As the Ghibli-ification of everyday life continues, the implications of AI-generated art extend beyond mere entertainment. The ease with which users can create and share these images raises questions about the future of artistic expression and the livelihoods of traditional artists. With the rise of AI tools, photographers and illustrators may find it increasingly challenging to protect their work from being reproduced without consent.
The situation is further complicated by advancements in AI technology that allow for the removal of watermarks and other protective measures. For instance, Google's Gemini 2.0 has demonstrated the ability to eliminate watermarks from images, posing a significant threat to artists who rely on these safeguards to protect their intellectual property.
In light of these developments, artists are urged to remain vigilant in protecting their work. OpenAI has introduced an opt-out mechanism, allowing creators to request that their work not be used to train the AI. However, the process has been criticized as cumbersome, requiring users to submit a form or use a button to express their preference.
As the debate surrounding AI-generated art continues to evolve, it is clear that the landscape of creativity is changing rapidly. The potential for AI to democratize art creation is exciting, but it also presents significant challenges that must be addressed. Artists, technologists, and policymakers must work together to navigate the complexities of intellectual property in the age of artificial intelligence.
OpenAI's new image generation feature has undoubtedly captured the imagination of users worldwide, but it also serves as a stark reminder of the need for ethical considerations in the development of AI technologies. As the company prepares for a future where AI plays an increasingly prominent role in creative industries, the questions of copyright, artistic integrity, and the rights of creators will remain at the forefront of discussions.
The implications of OpenAI's advancements are profound, as the company expects to earn $12.7 billion in revenue this year, further solidifying its position as a leader in the AI space. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be fascinating to see how it shapes the future of art and creativity.