Locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) poses significant challenges in clinical management, particularly regarding variability in treatment responses to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT). In a remarkable new study, researchers have developed a predictive biomarker that aims to improve treatment outcomes for LARC patients.
The study establishes a 32-gene pair signature (32-GPS) as a novel predictive biomarker necessary for better anticipating how individual patients respond to nCRT, which has been shown to reduce tumor volumes and enhance surgical outcomes. Despite the benefits of nCRT, only a fraction of patients—approximately 15-27%—achieve a pathological complete response (pCR), indicating a pressing need for effective predictive tools in managing this disease.
Identifying predictive biomarkers for LARC patients receiving nCRT is crucial, given the substantial variability in treatment response related to individual differences in gene expression. Current evaluation methods lack the precision necessary to reliably forecast who will benefit most from nCRT, leading some patients to endure unnecessary side effects from the treatment.
The authors of the article emphasized that “identifying new biomarkers to predict response to nCRT is imperative,” recognizing the urgent demand for tailored treatment strategies that can better serve patients’ individual needs.
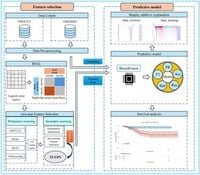
The study used an innovative two-step feature selection methodology combined with ensemble learning through the BoostForest model, yielding the 32-GPS. Initial screening involved employing four distinct feature selection methods—MultiDimensional Feature Selection (MDFS), Boruta, Monte Carlo Feature Selection (MCFS), and VSOLassoBag. This comprehensive approach allowed the researchers to identify and refine stable reversal gene pairs from LARC patient samples.
In tests, the 32-GPS achieved an impressive area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.983 and an accuracy rate of 0.988, underscoring its potential as a powerful prognostic tool. In the validation cohort, performance metrics remained robust, with an AUPRC of 0.785 and an accuracy of 0.898. The results indicated that the model’s performance significantly outweighed that of established predictive models, including Random Forest, Support Vector Machines, and XGBoost. The study found that “BoostForest achieved superior overall performance compared to Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and XGBoost.”
Using relative expression orderings (REOs) provided the necessary robustness against batch effects that hamper many predictive modeling efforts. The study's methodology enhances the reliability of the derived predictive factors by overcoming the limitations of traditional regression models that frequently suffer from noise sensitivity and multicollinearity. This new approach allows for a more precise identification of relevant gene pairs involved in drug responsiveness.
In addition to its methodological innovations, the study exhibits a strong commitment to predictive power in the context of clinical applications. For patients undergoing nCRT, pinpointing which genes are most predictive of treatment responses can profoundly inform clinical decisions, ensuring that patients are treated appropriately according to their unique biological profiles.
The findings of this research indicate a promising path forward in the realm of precision medicine, where treatment can be customized based on underlying genetic factors. As most flux occurs in patient responses, leveraging methodologies like the 32-GPS biomarker offers hope for improved clinical outcomes, and further research is warranted to validate and extend its applicability in broader clinical settings.
In conclusion, the development of the 32-GPS represents a significant advance in the quest for personalized medicine for LARC patients. With efforts aimed at optimizing predictive accuracy and treatment effectiveness, this study lays the groundwork for utilizing genetic insights to transform patient care.