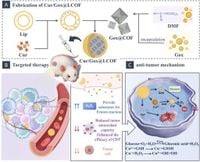
In a significant advance for breast cancer therapy, a novel cascade nano delivery system, known as Cur/Gox@LCOF, has been developed to enhance treatment outcomes. By effectively loading the potent anti-cancer agent curcumin and the enzyme glucose oxidase into a lipid copper-based organic framework, researchers have created a multifunctional platform that can improve therapeutic precision while reducing systemic toxicity.
Breast cancer remains a critical public health concern, with an alarming rise in incidence rates. In 2020, over 2.26 million new cases were reported globally, surpassing all other malignancies and underscoring the need for effective treatment methods. Current therapies, while sometimes effective, are often hindered by adverse side effects, leading to poor patient quality of life. The recent study highlights the potential of multimodal cancer therapies, specifically combining chemokinetics, chemotherapy, and starvation therapy, to substantially improve treatment efficacy.
The Cur/Gox@LCOF delivery system showcases a unique cascade mechanism, utilizing a combination of curcumin and glucose oxidase to enhance the body's natural oxidative response against cancer cells. The copper-based organic framework not only serves as a delivery vehicle but also catalyzes essential reactions that generate high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This in turn leads to increased cancer cell cytotoxicity, particularly effective in the harsh tumor microenvironment.
Characterized by its spherical morphology with an average diameter of 80 nm, the designed nanoparticles exhibit pH-responsive properties, allowing for controlled release of therapeutics directly within tumor tissues. The encapsulation process ensures stability under physiological conditions while remaining sensitive to the acidic environment typically found around tumors.
Researchers performed a series of in vitro tests to validate the effectiveness of Cur/Gox@LCOF. The nanoparticles significantly enhanced ROS production, inducing cytotoxic effects on breast cancer cells in laboratory experiments. Additionally, in vivo studies with tumor-bearing mice demonstrated substantial inhibition of tumor growth, leading to a higher survival rate among treated subjects. Mice administered the Cur/Gox@LCOF showed the smallest tumor volumes and weights, highlighting the potent anti-tumor efficacy of this innovative approach.
Furthermore, the safety profile of the Cur/Gox@LCOF system presents favorable outcomes. In toxicity studies, the hemolysis rate remained below 5% at various concentrations, indicating good biocompatibility. Histological examinations of treated mice organs revealed no significant damage or adverse inflammatory responses, reinforcing the potential for clinical application.
In the future, the focus will be on optimizing the Cur/Gox@LCOF system to enhance targeting specificity within tumors. The integration of tumor-specific ligands could further improve drug delivery efficacy, paving the way for more effective breast cancer treatments.
This innovative cascade nano delivery system represents a promising avenue in the quest for advanced cancer therapies. As research continues to advance, the hope is to translate such findings into clinical settings, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.