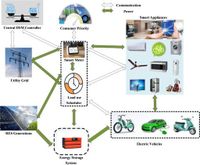
The exponential deployment of electric vehicles (EVs) in the residential sectors in recent years allows better energy utilization in the decentralized and centralized levels of distribution systems due to their bidirectional operation and energy storage capabilities. However, to execute these, it is necessary to adopt residential demand side management (RDSM) to schedule energy utilization effectively to fetch economical and efficient energy consumption and grid stability and reliability, particularly during peak load conditions. The paper aims to formulate a robust and efficient RDSM technique to provide an energy utilization scheduling considering various influential factors and critical roles of EVs in RDSM.
A Binary Whale Optimization Algorithm (BWOA) approach is proposed as an efficient algorithm for EV’s impact on the RDSM for better energy scheduling. A single-objective formulation is presented with detailed modelling considering economic energy utilization as the primary objective with all possible equality and inequality system operational constraints. Secondly, the impact of EVs on the RDSM is studied from various perspectives in result analysis, considering EVs as load, storage devices, and different bidirectional modes of operation with other vehicles, residential components, and grids.
In addition, the EVs role and the mutual influence with the integration of renewable energy sources (RES) and energy storage devices (ESDs) are extensively analyzed to provide better residential energy management (REM) in terms of economic, environmental, robust, and reliable points of view. The load priority based on consumer choice is also incorporated in the formulation. Extensive simulation is done for the proposed approach to show the effect of EVs on REM, and the results are impressive to show the EV’s role as a load, as a storage device, and as a mutually supportive device to RES, ESD, and grid.
The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) used in residential sectors makes it possible to integrate them into residential demand-side management (RDSM) to significantly impact overall performance in terms of energy utilization from various perspectives. The EVs as the load can act as load shifting load during the off-peak period that makes the demand curve flat, reducing energy demand during peak hours and establishing optimal energy utilization. The EVs can support grid stability, flexibility, and overall energy regulation along with other energy storage devices (ESD) and renewable energy sources (RES), even in the case of residential sectors when the consumers act as prosumers during the excess energy availability for a certain period in case of high EV adoption rates.
In addition, the EVs can act as storage devices and help implement an optimal RDSM along with the RES and ESD, which can benefit both consumers and utility. Apart from that, the time-of-use (ToU) pricing models with EV support can bring efficient energy consumption patterns that result in cost savings in energy utilization. The RDSM plays a crucial role in the case of excessive EV charging penetration into the distribution system. It forces to focus on infrastructure planning to accommodate larger charging demand and install smart meters and charging infrastructure to provision DSM strategies effectively.
The EVs support environmental sustainability goals like carbon emission reduction, independence of fossil fuels, and enhancement of efficient transportation facilities. The implementation of DSM incorporating EVs needs adequate data management and privacy related to charging patterns, electricity consumption, and grid conditions to ensure consumer privacy and security while leveraging this data to optimize DSM strategies effectively. Regulating energy utilization effectively with EVs in residential sectors changes consumer behavior. This requires adopting an efficient DSM technique to encourage EV owners to maximize the benefits following the information and incentives.
Regulatory frameworks are necessary to support the effective integration of EVs in RDSM, including developing standards for interoperability, establishing fair pricing mechanisms, and ensuring equitable access to DSM benefits for all consumers. All the above indicates that the implementation of EVs in residential DSM facilitated the opportunities to improve the grid efficiency, promote RES integration and cost savings, and support sustainable transportation initiatives. However, it also needs careful planning, investment, and load scheduling to realize its full potential while addressing associated challenges.
The study proposes an optimal RDSM-based energy utilization scheduling concerning various aspects of EV integration in the residential sector. It is essential to integrate the EVs in the RDSM as a load through strategic planning, particularly during the peak and off-peak periods, to regulate the electricity patterns and constraints in the residential settings. The EVs play a crucial role in the residential load scenario, as energy consumption and storage devices during off-peak and peak periods, respectively. However, many critical factors need to be incorporated into the energy scheduling in the RDSM to utilize EVs in both roles effectively.
The research focuses on identifying off-peak and peak hours while considering uncertainties and user priority. Secondly, charging scheduling for EVs is facilitated through time-of-use (ToU) pricing plans as prescribed by utilities, which results in optimal economic energy utilization. This is achievable when the residential sector has the best intelligent charging infrastructure and grid communication for dynamic adjustment of charging schedules to maximize efficiency and grid support.
The results indicate that integrating EVs within residential demand-side management frameworks yields additional operational benefits, including peak load reduction, meeting unpredictable demand, and supporting diverse energy consumption priorities. The interaction between EVs, renewable energy sources, and energy storage systems demonstrates the potential for enhancing reliability and sustainability in energy management. These elements are crucial for achieving effective energy scheduling and improving grid resilience while ensuring cost-effectiveness for consumers.
The overall findings underscore the transformative role of EVs in modern residential energy systems, where technological advancement and strategic planning pave the way for a sustainable and efficient energy future.