A novel sealing material combining multi-walled carbon nanotubes, xanthan gum, and magnesium oxide has been developed, showcasing significant improvements in strength and efficiency for preventing spontaneous coal combustion in mining operations. This new composite, known as MXM-CCC, addresses the critical safety issues posed by spontaneous combustion of coal, which has been the cause of over 90% of mine fires. The study, published on March 20, 2025, demonstrates that MXM-CCC can significantly enhance sealing effectiveness through optimized mechanical performance.
In 2023, China produced an astounding 47.1 billion tonnes of raw coal, leading to increasing safety concerns related to mined-out areas that have become hotspots for spontaneous combustion. The primary technique for managing such hazards revolves around preventing oxygen supply, thereby controlling gas leaks which could ignite fires. Researchers have proposed the MXM-CCC to tackle these challenges.
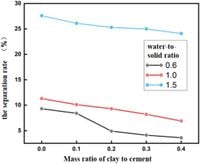
The study revealed that the optimal water-to-solid ratio for the multi-component system was determined to be 0.6. Additionally, when the mix included 1.5% xanthan gum, 5% magnesium oxide, and 1.39% MWCNTs, the compressive strength of MXM-CCC reached 18.60 MPa, with a flexural strength of 3.89 MPa. The added materials work synergistically to improve the mechanical properties while also enhancing the pore structure, which is crucial for effective sealing in coal mining environments.
Characterization analyses indicated that MXM-CCC possesses a porosity of 17.29%, with important pore sizes ranging from 2.00 nm to 50 nm, making up 71.46% of the total. This specific pore distribution aids in effectively blocking gas leaks. The use of MWCNTs particularly accelerates hydration reactions, enhancing not only the strength of the material but also its integrity under various conditions.
The improved sealing technology has important implications for the safety practices in the mining industry. The authors of the article stated, "By incorporating MWCNTs, the hydration reaction accelerates, significantly improving the mechanical properties of the sealing material." This finding emphasizes that the advanced composite can withstand harsh mining conditions far better than traditional sealing materials.
Prior to this development, many organic sealing materials have been found inadequate due to flammability and high costs. On the other hand, traditional modified cement mortar materials often suffer from low strength and potential for cracking, which hinders their sealing efficacy. Through the innovative combination of MWCNTs, XG, and MgO, MXM-CCC stands out as a promising solution that bolsters the durability and mechanical properties of sealing materials.
Ultimately, the study concludes that by reducing porosity and optimizing pore size distribution, MXM-CCC achieves superior mechanical properties. The addition of MWCNTs is particularly noteworthy as it acts as a bridge connecting various hydration products, improving overall performance and stability. Xia, a researcher involved in the study noted, "This study shows the potential of using nano-filling agents to enhance material density and performance in critical sealing applications."
The introduction of such innovative materials in coal mining reflects a significant step toward better safety measures in the industry. As MXM-CCC continues to undergo testing and refinement, there may be opportunities for further research to explore its capabilities and applications within other areas of construction and underground operations.