In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled the critical role of RNA processing genes in predicting outcomes for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), a type of cancer notorious for its treatment challenges and high recurrence rates. The findings highlight LSM5 and RBM20 as significant prognostic markers that could revolutionize patient management and therapeutic strategies.
NPC, which primarily arises in the nasopharynx, presents distinct clinical challenges due to its high prevalence in certain regions, particularly East and Southeast Asia, where more than 70% of cases occur. Current treatments, including concurrent chemoradiotherapy, are often insufficient, leading to treatment failures and poor patient outcomes. As approximately 129,000 new cases of NPC are documented globally each year, innovative strategies are urgently needed to improve prognosis and treatment response.
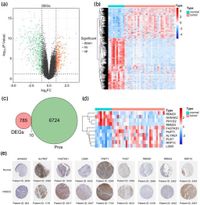
Identifying the molecular factors that contribute to NPC's progression is crucial for developing targeted therapies. In this recent research, scientists conducted bioinformatics analyses on transcriptomic datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus to identify differentially expressed RNA processing genes (DE-RPGs) associated with NPC. The study identified 10 pivotal genes, among which LSM5 and RBM20 emerged as pivotal biomarkers. The authors noted, "LSM5 is identified as a new adverse biomarker in NPC, with implications for targeted therapy and prognosis improvement." This highlights the potential of RNA processing factors not only in enhancing prognostic accuracy but also in informing treatment decisions.
The research team employed advanced techniques, including Cox regression modeling, to establish a prognostic model based on LSM5 and RBM20. Remarkably, the study found that higher expression of LSM5 correlates with worse patient prognosis, while RBM20 appears to have a protective role against cancer progression. They constructed a risk score model demonstrating that patients with higher LSM5 expression faced significantly poorer disease-free survival rates, affirming the gene's prognostic capability.
Additionally, the analysis revealed significant correlations between the expression of these RNA processing genes and various immune cell types infiltrating the tumor microenvironment. Notably, the presence of immune cells, such as CD8+ T cells, was associated with improved survivability in patients with NPC. In this context, the authors observed, "Furthermore, LSM5 expression was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and identified as a new unfavorable prognostic biomarker." These insights into the immune landscape could pave the way for more effective immunotherapeutic strategies in NPC.
The team also evaluated the sensitivity of NPC cells to different chemotherapeutic agents based on the risk scores determined by LSM5 and RBM20 expression levels. Their analysis indicated that patients classified within the low-risk group demonstrated greater sensitivity to 55 specific chemotherapy drugs, suggesting that tailored treatment regimens could substantially benefit these individuals.
Through comprehensive experiments including reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western Blot analyses, the researchers validated the expression patterns of LSM5 and RBM20 in both NPC tissues and cell lines. The results indicated a consistent trend, supporting the clinical relevance of these gene expressions in NPC prognosis. The study acknowledged that LSM5 and RBM20 are not previously characterized in the context of NPC, marking a novel step toward understanding the disease biology.
While the research showcases promising results, the authors recommend further investigations into the functional roles of these RNA processing genes and their interactions within the tumor microenvironment. Such studies are essential for validating the utility of LSM5 and RBM20 as therapeutic targets and biomarkers.
In conclusion, this pioneering research highlights the importance of RNA processing genes, particularly LSM5 and RBM20, in dictating the prognosis and potential treatment pathways for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The findings hold promise for enhancing the precision of therapeutic approaches in NPC, ultimately aiming to improve survival and quality of life for patients.