A new framework aimed at cloud-enabled e-commerce negotiations has emerged, designed to enhance the trustworthiness and efficacy of negotiations among participants, including consumers, brokers, and service providers. This innovative framework utilizes a Bayesian-based Adaptive Probabilistic Trust Management Model to effectively gauge trust levels, thus fostering improved negotiation outcomes.
Negotiation within cloud markets is increasingly complex, and establishing trust has become one of the foremost challenges. The framework targets the intricacies of service provision by implementing a system that dynamically assesses and ranks service provider agents based on their historical negotiation performance metrics, specifically focusing on success rate, cooperation rate, and honesty rate. "This adaptive model dynamically ranks the service provider agents by estimating the success rate, cooperation rate and honesty rate factors to effectively measure the trustworthiness among the participants," wrote the authors of the article.
At its core, the cloud-enabled e-commerce negotiation framework (CENF) seeks to optimize participants' utility value and success rate by establishing a cooperative environment facilitated through an agent-based architecture. The negotiation process follows an alternate offer protocol mechanism, which enhances communication and decision-making among participants.
The architecture includes integral components, namely service consumer agents (SCA), intelligent third-party broker agents (ITBA), and service provider agents (SPA). In this framework, ITBAs leverage the Bayesian model to generate trust scores for service providers based on previous negotiation engagements. Not only does this system minimize potential conflicts during negotiations, but it also streamlines the process by ensuring that parties involved offer competitive and honest deals.
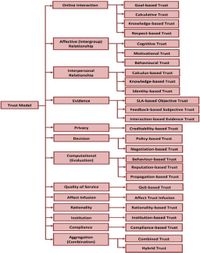
Integral to the operation of this framework is the establishment of trust, which is defined quantitatively through the Bayesian-based trust management model. Feedback from participants assists in converting subjective experiences into quantitative data, feeding back into the trust evaluation process. This model incorporates features such as a trust manager, trust database, feedback collection agent, trust monitoring agent, and trust decision agent. As a result, negotiation outcomes are not solely dependent on the quality of service or offer presented, but are heavily influenced by the perceived reliability of the service provider.
The study emphasizes the importance of employing Bayesian learning to represent the distribution of trust rankings effectively. The model clearly delineates how trust values can be influenced by historical negotiation interactions, adjusting dynamically as new data from concurrent negotiations are introduced. This adaptability aids in selecting trustworthy service providers while maximizing efficiency during cloud service negotiations.
The experimental evaluation was conducted using the JADE (Java Agent DEvelopment Framework) simulation tool, which mimicked real-time negotiation scenarios in cloud computing environments. Observations demonstrated that the proposed framework performs significantly better than existing negotiation architectures, such as the negotiation framework architecture (NFA) and the automated dynamic SLA negotiation framework (ADSLANF). Among the notable findings, the projected cloud-enabled e-commerce negotiation framework (BCENF) showed improvements in total negotiation time, reduced communication overhead, and heightened success rates across various rounds of negotiation. With 50 negotiation rounds, the BCENF outperformed its predecessors, and this trend of improvement continued with increasing rounds, indicative of its robust design and implementation.
As the authors pointed out, "The proposed trust management model leverages the negotiation process of ITBAs without any conflict with the SPAs." This underscores the framework's capacity not only to facilitate efficient negotiations but also to enhance the collaborative environment necessary for effective service provisioning in cloud markets.
While considerable advancements have been made in cloud-based negotiation frameworks, the study acknowledges ongoing challenges, including negotiation protocol optimization and minimizing communication overhead during concurrent negotiations. Future improvements might leverage machine learning techniques to further bolster the adaptability and efficacy of trust management in negotiations, a promising avenue as cloud service demands continue to evolve.
Ultimately, the introduction of this broker-based cloud-enabled e-commerce negotiation framework aligns with the increasing complexity of cloud transactions and holds significance for both cloud service users and providers alike. Strengthening trust in these digital transactions stands to benefit all parties involved—privileging transparency and encouraging a more cooperative marketplace.