In the quest for maximizing shale oil extraction efficiency, researchers have proposed an innovative evaluation method that delves into the fractal characteristics of conventional logging curves. This newly developed approach aims to address the inherent challenges associated with traditional logging evaluation methods, which often suffer from complexity and inefficiency.
The study conducted by a team of scientists at the Qinghai Oilfield sheds light on the limitations of existing shale oil reservoir evaluation techniques, which are complicated by a myriad of parameters—over 50 in some cases—and discrepancies between evaluation results and actual production outcomes. A need for a more streamlined and effective evaluation method has become increasingly apparent.
By leveraging wavelet transform techniques, the researchers were able to reduce noise in high-frequency signals from conventional logging curves. The analysis of 63 fractured sections from three horizontal fractured wells in the Yingxiongling shale oil reservoir involved multifractal spectrum analysis and R/S analysis aimed at extracting two critical parameters: the multifractal spectrum width (∆α) and fractal dimension (D) from four conventional logging attributes: natural gamma logging (GR), acoustic time difference logging (AC), density logging (DEN), and neutron logging (CNL).
A multi-attribute comprehensive fractal evaluation index was established through the integration of production profiles from post-fracturing tracer monitoring and grey relational analysis. The findings indicated that a high-yield well section after Class I layering matched a comprehensive fractal evaluation index where 0.75 < ∆α' < 1 and 0 < D' < 0.25, while a low-production well section fell under 0 < ∆α' < 0.35 and 0.8 < D' < 1.
The newly proposed evaluation method holds substantial promise for achieving precise evaluations of shale oil production capacity, addressing the escalating demands of unconventional reservoirs that require intricate development strategies. In terms of efficacy, this methodology has demonstrated a 31.9% increase in accuracy compared to conventional models during its application to shale oil sweet spot prediction.
China has made strides in establishing the “Shale Oil Geological Evaluation Methods” (GB/T38718-2020) standard, further supporting efforts to enhance shale oil resource development. The comprehensive fractal evaluation not only simplifies the extensive process of conventional evaluations but also offers robust support for optimizing exploration strategies.
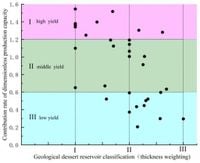
In this study, the team focused particularly on the fracture monitoring data from the CP2 and CP4 wells within the Heroes’ Ridge shale reservoir. They classified a dimensionless productivity rate greater than 1.2 times as high yield (Class I), less than 0.6 as low yield (Class III), and rates in between as medium yield (Class II).
Such classifications have proven invaluable in guiding effective volumetric fracturing, with the software-based prediction models boasting higher predictive accuracy. The evaluation method encompasses three primary classes that identify high-yield fractured well sections exhibiting optimal permeability and fluid distribution.
The continuous advancement of this fractal evaluation method showcases the interplay between mathematical modeling and geological data that underscores the unique characteristics of shale reservoirs. The integration of machine learning algorithms has further refined the accuracy of predicting physical property parameters for these shale reservoirs.
In summary, the study emphasizes that this novel approach not only enriches the understanding of shale oil reservoirs but also serves as an instrumental tool in the effective management and extraction of fossil fuel resources for the future.