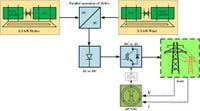
A novel Adaptive Predictive Virtual Synchronous Generator (AP-VSG) control strategy is set to revolutionize how renewable energy sources integrate into existing power grids, promising greater stability and reliability as nations accelerate their transition to cleaner energy solutions. The innovative approach addresses a critical gap in current grid management by introducing adaptive inertia and damping mechanisms, coupled with advanced predictive optimization techniques specifically tailored for parallel-connected Self-Excited Induction Generators (SEIGs).
The continuing shift towards sustainable energy underlines the urgency of integrating renewable sources such as wind and solar into power grids. Traditional power systems, historically reliant on large synchronous generators which inherently provide stabilizing inertia, face significant challenges due to the variability of renewable sources. Without sufficient inertia, grids become more susceptible to frequency fluctuations, leading to potential instability. The AP-VSG control strategy offers a powerful solution to this pressing challenge, mimicking the characteristics of synchronous generators to enhance stability.
One of the hallmark features of the AP-VSG is its ability to adaptively control virtual inertia, exhibiting a range from 1 to 4 seconds and damping coefficients that vary between 20 and 65 per unit (pu). This adaptability allows the system to respond dynamically to variations in grid frequency and the Rate of Change of Frequency (RoCoF). Experimental validations of the strategy demonstrated a significant reduction in maximum RoCoF from ± 0.48 Hz/s to ± 0.21 Hz/s, along with a 33% improvement in frequency nadir during tests involving both 2.2 kW and 5.5 kW SEIGs.
The experimental framework showed that the AP-VSG maintained a critical current limit of 1.5 pu while providing reactive support up to 0.8 pu, ensuring that stability was preserved even under fault conditions. Moreover, the multi-objective optimization process resulted in a substantial 36.7% reduction in control effort, which helps alleviate the computational demands typically associated with traditional control strategies.
What sets the AP-VSG apart from conventional Virtual Synchronous Generators is its distinct operational capability: while traditional methods often necessitate multiple DC-to-AC conversion stages that can complicate system architecture and reduce efficiency, the AP-VSG allows for direct parallel operation in the AC domain. This innovation not only cuts down on the necessary system complexity but also enhances overall performance, a critical aspect as renewable energy penetration continues to escalate.
In practice, the AP-VSG's advanced control strategy improves upon previous methods by continuously learning from and responding to grid conditions based on real-time data. As grid complexities and energy demands grow, the adaptive nature of this control strategy becomes increasingly essential. "This work not only improves the individual performance of SEIGs but also contributes to a collective improvement in grid stability and power quality," noted the authors of the article.
By achieving a 56% reduction in maximum RoCoF and ensuring voltage recovery post-disruptions within 100 milliseconds with harmonic distortion (THD) below 3%, the system demonstrates a robust response to a variety of grid disturbances. Such capabilities position the AP-VSG control strategy as a pivotal development within the energy sector, particularly as countries strive to meet ambitious renewable energy targets aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Looking forward, the introduction of AP-VSG control is indicative of the ongoing innovations necessary for adapting power systems in the face of changing energy landscapes. The results present promising opportunities for the technology to support not only frequency regulation but also improve voltage stability and overall energy quality across progressively renewable-rich systems.
The broader implications of this research are profound, with the potential for AP-VSG to play a key role in supporting a more resilient and efficient energy future. Enhancing power system stability amidst the growing reliance on renewable energy sources is not just a step forward; it's a necessity for ensuring sustained energy security. As these challenges are addressed with innovative solutions like the AP-VSG, they pave the way for a cleaner, more reliable grid capable of meeting the global energy demands of tomorrow.