The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and various countries, particularly in Europe, are reshaping the landscape of international commerce. Recent tariff increases imposed by the Trump administration are expected to have a limited impact on the Italian economy, according to a study by Unimpresa’s research center. This is largely due to the high quality of Italian exports, the resilience of large companies, and the stability of profit margins within the sector.
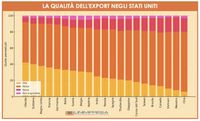
Currently, only about a third of Italian companies export to the United States, which amounts to approximately 34,000 businesses. These companies generate over 50% of their exported value from enterprises with more than 250 employees, which are better equipped to absorb economic shocks. Italian goods account for 10% of total exports to the U.S., with a significant portion categorized as high-end products. Specifically, 43% of these exports are in the high-end category, 49% in the mid-range, and only 8% are low-end products that are more sensitive to price fluctuations.
According to Unimpresa, the gross operating margin for Italian companies exporting to the U.S. averages around 10%, with these businesses generating about 5.5% of their total revenue in the American market. The study suggests that the newly proposed tariffs, ranging from 20% to 25%, could lead to a 1% reduction in the total revenue of exporting companies and a decrease in profit margins of up to 0.5 percentage points for 75% of those affected.
The sectors most vulnerable to these tariff hikes include pharmaceuticals, which account for 24% of the added value linked to the U.S. market, followed by shipbuilding and aerospace at 15%. Other industries, such as furniture, electronics, fashion, and automobiles, contribute between 6% and 8% to the export value. Smaller companies, often lacking diversification and operating with thinner margins, are particularly at risk. "It is essential to monitor the evolution of the situation and consider targeted support for the most exposed companies while simultaneously encouraging market diversification," noted Giuseppe Spadafora, Vice President of Unimpresa.
While the impact of the tariffs is expected to be manageable for larger companies, smaller enterprises could face critical challenges. The Italian manufacturing system is structurally resilient enough to withstand this new wave of American protectionism, at least in the short term. However, specific vulnerabilities remain, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises heavily reliant on the U.S. market.
In a related discussion, the Italian export credit agency, Sace, highlighted the importance of diversifying trade routes. Italy exports around 85 billion euros worth of goods to 14 countries identified as 'Gate' countries, representing about 13% of total Italian exports. These markets include significant trading partners such as the United Kingdom, Turkey, and Japan, which recorded notable increases in imports from Italy in 2024. For instance, the UK saw a 5.3% increase, while Turkey's imports surged by 23.9%.
Moreover, Sace recently launched the "Rupie Express" initiative in India, which aims to facilitate Italian exports by guaranteeing 200 million euros in financing for Indian buyers interested in sourcing from Italy. This move reflects a broader strategy to strengthen Italy's position in global supply chains and mitigate risks associated with overreliance on the U.S. market.
As the discussion continues, Silvia Carpanese, a regional trade department head in Veneto, expressed concerns regarding the broader implications of Trump's tariff policy. "The tariff policy is having a disruptive impact on international markets, particularly in Europe, which is one of the most significant export markets globally," she stated. Carpanese emphasized the importance of finding a cooperative approach with the U.S. to safeguard Italian exports while also reinforcing European strategic assets.
The Veneto region, in particular, has significant export figures, with a total value of 7.3 billion euros, driven by cities like Vicenza, which alone accounts for over 2.2 billion euros in exports. The region excels in high-quality products, ranging from food and wine to mechanical components and chemicals. However, Carpanese warns against retaliatory trade measures, which could further destabilize the global market.
In light of these developments, the European Commission has proposed a "tariffs 0 for 0" agreement to the U.S. in an effort to eliminate tariffs on all industrial goods. Should these negotiations fail, the EU may resort to the 'anti-coercion' measures introduced in 2023 to protect its economy from adverse effects stemming from U.S. tariffs.
As the Italian economy navigates these turbulent waters, the focus remains on sustaining growth and protecting vulnerable sectors. The potential closure of small businesses, particularly in regions like Padova, where 60 shops have shut down in just four months, highlights the urgent need for strategic interventions. Carpanese noted that issues such as high commercial rents and generational transitions in business ownership are exacerbating the challenges faced by local enterprises.
In summary, while the Italian export market grapples with the implications of U.S. tariff policies, the resilience of larger companies and the strategic diversification of trade routes may offer a buffer against potential downturns. The emphasis on quality exports and the proactive measures being taken by the Italian government and trade agencies could ultimately determine the long-term sustainability of Italy's economic landscape amid global trade tensions.