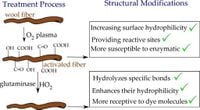
Recent advances in textile science have directed attention to the surface modification of wool fibers, highlighting the need for eco-friendly practices. A new study published on March 17, 2025, sheds light on the effectiveness of combined plasma and enzymatic treatments aimed at enhancing wool's dye absorption capabilities and mechanical properties.
The investigation, conducted by researchers at the University of Birjand, examines how these treatment methods can effectively optimize wool fibers, which have long been recognized for their versatility and durability. Wool fibers, derived from the hair of sheep, possess natural hydrophobic properties attributed to their complex structure of cuticle scales made of keratin. Traditional methods for enhancing dye uptake often involve chemical treatments, which can induce environmental concerns.
This study evaluated various surface treatments, including the use of plasmas and biodegradable enzymes such as glutaminase and protease. The researchers employed atmospheric pressure glow discharge devices for plasma treatment, which operates under mild conditions and does not require hazardous chemicals—a key advantage over conventional chemical treatments.
Utilizing wool fibers with an average diameter of 34 μm, the team performed plasma treatment at 85 V and 15 MHz for five minutes. Enzyme treatments employed 0.5% glutaminase or protease solutions, with specific pH and temperature controls. After treatment, the structural changes introduced were analyzed using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
SEM images revealed significant morphologic alterations, with treated fibers displaying increased surface roughness and disruption of cuticle scales. Notably, the authors of the article pointed out, "The synergistic effects of combined plasma and enzyme treatments led to improved surface modification, color properties, and mechanical performance of wool fibers." This structural modification is primarily responsible for the enhanced absorbance of various dyes.
Colorimetric analysis showed a marked increase in fiber lightness and whiteness after treatment. Protease-treated fibers achieved the highest Whiteness Index (WI) of 78.24, underscoring the effectiveness of enzyme treatments in imparting cleanliness and clarity. Comparatively, plasma treatment alone yielded lower WI scores due to slight surface etching. The lightness and optical characteristics were also favorably altered when enzymatic treatments were combined with mordants like alum.
The color strength, calculated using the K/S value, demonstrated significant improvements across all treatment combinations, indicating enhanced dye uptake and retention. The combined use of glutaminase with plasma treatment exhibited the highest K/S value of 20.3, reflecting superior dye binding capabilities. This performance aligns with the findings of previous studies emphasizing the benefits of enzyme-based treatments.
Mechanical tests affirmed these findings; plasma-treated wool showed improved tensile strength, promoting durability without sacrificing flexibility. The maximum stress recorded for plasma-treated wool was slightly higher than the untreated control, setting the foundation for future applications. The potential for synergy between treatments was apparent, with combinations creating optimal pathways for dye interaction and mechanical resilience.
These advancements present both practical solutions and sustainability pathways for the textile industry. The combination of plasma and enzymatic treatments emphasizes the shift toward more responsible practices and green chemistry principles.
Overall, the study indicates significant potential for optimizing wool fiber treatments, addressing traditional limitations, and creating enhanced performance characteristics. The authors stated, "These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing wool fiber treatments in textile applications," reaffirming the contributions of their research toward sustainable textile practices. This study not only advances the technical knowledge of wool treatment methodologies but also aligns with industry efforts to promote ecological responsibility within fabric production.