The rapid advancement of wireless communication technology necessitates innovative approaches to RF modulation, leading to the development of a new hardware architecture that enhances pulse width modulation (PWM) resolution. This breakthrough, proposed by a team of researchers, features a jitter-enhanced PWM design that allows for substantial improvements in signal quality while minimizing the required operating frequency.
At its core, the technology focuses on the RF transmitter, a critical component of radio frequency communication systems that encodes information into RF signals. The novel jitter-enhanced architecture distributes phase jitter evenly across each radio frequency cycle, effectively improving the modulation resolution by up to 5.32 bits while maintaining an excellent error vector magnitude (EVM) performance of -41.21 dB. Notably, this new method enables the use of significantly lower PWM frequencies, down to 400 MHz, compared to traditional requirements.
Current mainstream quantization techniques in RF communication include Delta-Sigma modulation (DSM) and pulse width modulation (PWM). While DSM is celebrated for its accuracy, it requires a high oversampling rate, making it less feasible for specific applications. On the other hand, PWM is favored for its simplicity, lower hardware costs, and lower clock rate requirements. The novel architecture demonstrates that by leveraging jitter, the performance of traditional PWM can be revamped, addressing issues related to moderate modulation resolution at high frequencies.
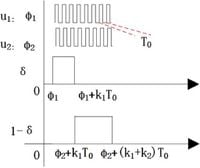
The research encompasses detailed evaluations of the jitter-enhanced PWM algorithm, which builds on foundational principles outlined in prior studies. The technology strategically utilizes phase information modulation through a carefully designed delay line architecture that processes baseband signals into RF signals. The authors of the article highlight that this method offers a remarkable improvement over conventional schemes, exemplifying a transformative approach for RF digital transmitters.
The verification of this jitter-enhanced system was conducted using a test platform based on the Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ series RFSoC ZCU111 model FPGA board. This setting enabled researchers to assess the performance of the transmitter against standard benchmarks. The conducted experiments, utilizing a baseband frequency of 2 MHz and an RF frequency of 20 MHz, underscored the architecture's capacity to deliver reliable communication under practical conditions.
The results from comparative analyses indicate that the jitter method results in better demodulation effects than systems not employing these techniques, particularly when operating at 200 MHz and above PWM frequencies. Additional tests reinforced that as the RF frequency to baseband frequency ratio increases, the performance improves significantly. This is crucial for modern applications demanding both high efficiency and low power consumption in RF communications.
Utilizing a total system power consumption of 1.118 watts, mainly attributable to static power consumption components, the architecture achieves remarkable power efficiency without sacrificing performance quality. The static power is primarily derived from core logic leakage and I/O bank quiescence, indicating a balanced integration for effective resource utilization.
Moving forward, the research team emphasizes the ongoing potential for improved designs. Future explorations are said to focus on integrating multilevel PWM technology to further enhance modulation resolution while addressing inherent design complexities. The team is optimistic about adapting the architecture for higher frequencies and broader bandwidth applications, guided by optimization efforts surrounding logical simplifications and hardware resource allocations.
In summary, the introduction of this jitter-enhanced PWM architecture marks a significant step in reducing frequency requirements in RF transmitting systems. The efficient modulation techniques can bring transformative improvements not only to embedded systems but also to a range of wireless communication applications. By achieving high performance with reduced physical parameters, this innovative framework is set to push the boundaries of RF communication technology.