Marine microbes play a crucial role in sustaining elemental cycles, as they are responsible for key geochemical processes such as organic carbon remineralization, nitrogen cycling, and atmospheric oxygen production. A novel study has introduced a powerful new tool, named 'Ayu', that utilizes machine learning to predict and identify secreted proteins from these marine microorganisms in ways previously unachievable.
In their quest to understand the marine secretome—the collection of proteins secreted by microbes—scientists often faced challenges due to the limitations of current biochemical methods. These methods, which typically rely on complex techniques and require cultivation of the organisms in laboratory settings, often fall short, as many marine bacteria cannot thrive outside their natural environments. Consequently, the secrets of how these organisms interact with their surroundings have remained largely unexplored.
By analyzing the adaptations of marine proteins and employing advanced data analysis techniques, the authors of the study developed Ayu to effectively characterize the proteins within the secretome, significantly broadening the understanding of microbial capabilities in oceanic ecosystems. Ayu stands out by relying on evolutionary adaptations to the marine conditions rather than homology predictions, allowing for superior performance in identifying more secreted proteins than conventional methods.
Utilizing a vast dataset derived from the Tara Oceans expedition—which included various samples of marine microbes taken from different oceanic regions—Ayu has been shown to recover quantities of protein that exceed traditional tools by more than double. This capability of revealing previously hidden components of marine microbial life underscores the profound impact of such technologies on marine biology.
In practical terms, this means that marine biologists can now better quantify and understand how these unseen proteins contribute to critical processes in the ocean, including nutrient cycling and biochemical interactions between organisms. Given that microbial activity is expected to play an increasingly significant role in response to changing environmental conditions, such insights are timely and necessary.
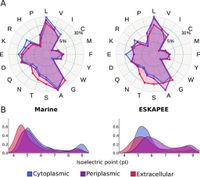
The development of Ayu involved sophisticated statistical analyses, particularly examining the amino acid composition and properties of proteins secreted by prokaryotic organisms. Findings revealed distinct patterns in the distribution of various amino acids, highlighting how proteins evolve to meet the physical and chemical challenges presented by the marine environment.
According to the authors, this innovation does not just enhance the field of metagenomics and proteomics; it also represents a paradigm shift regarding how scientists can interpret the secretome within marine contexts. Future applications of Ayu are expected to facilitate significant advancements in understanding microbial ecology and biochemistry, especially amid ongoing climate challenges.
This research not only equips marine scientists with greater tools but also provokes further inquiries into the complex roles that microbial secretions may play. Untapped areas such as interactions among microbial communities and their impact on oceanic processes remain ripe for exploration, making Ayu an exciting leap toward unraveling the mysteries of the ocean's hidden workings.
Ultimately, this study exemplifies the powerful intersection of machine learning with marine biology, paving the way for future innovations that may unlock further secrets of the marine environment and enhance our understanding of fundamental ecological processes.