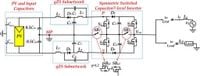
In a groundbreaking advancement for renewable energy, researchers have developed a new topology called the quasi-Z-Source Switched Capacitor Seven Level Inverter (qZ-SC7LI), which effectively mitigates inrush current, enhances voltage gain, and eliminates leakage currents common in photovoltaic (PV) applications.
The qZ-SC7LI represents a fusion of a symmetric single-phase Switched Capacitor Multilevel Inverter (SC-MLI) and a quasi-Z-source (qZS) network, showcasing significant improvements in performance metrics essential for grid-tied photovoltaic systems.
One of the key issues addressed by this innovative design is the leakage current, a substantial challenge faced by transformerless PV inverters that can pose safety risks and degrade system performance. Due to the inherent symmetry and proper configuration of the qZ-SC7LI, leakage currents have been reduced to a peak of approximately 3 mA, well below the safety threshold of 300 mA peak-to-peak as recommended by industry standards.
This new inverter design allows for adjustable voltage gain and ensures continuous input current, thus optimizing the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) process in PV applications. The results from a 1.2 kVA lab-scale prototype demonstrate that the qZ-SC7LI achieves an estimated efficiency of 95.4% at maximum load, making it a competitive alternative to existing inverter technologies.
Moreover, the enhanced design minimizes inrush currents during capacitor charging by employing a modified modulation technique that reduces the variation of output voltage. This technique enables the inverter to deliver a seven-level staircase AC voltage that maintains a total harmonic distortion (THD) significantly lower than conventional systems.
Inverter output tests revealed a peak voltage approximately 1.5 times the input voltage under specific conditions and showed improvements in operational stability under variable loads.
As renewable energy adoption continues to increase, the implications of this research extend to broader applications, promising a more efficient integration of solar energy into electrical grids worldwide. Future studies are suggested to explore further the compatibility between various Z-source networks and cutting-edge MPPT algorithms to enhance the scalability and robustness of PV systems.
In conclusion, the qZ-SC7LI provides a versatile and efficient solution ideal for modern PV applications, offering benefits of reduced leakage current, adjustable voltage gain, and heightened efficiency, thereby paving the way for future advancements in solar inverter technology.