In a significant development for healthcare quality management, a study has demonstrated that implementing the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) system in the assembly of reusable medical devices can dramatically reduce assembly defects and improve user satisfaction.
Conducted in a central sterile supply department (CSSD) at West China Second University Hospital, researchers compared 35,841 packages of reusable medical devices assembled before the HACCP implementation (January to June 2023) with 36,159 packages assembled after its implementation (July to December 2023). The results were striking, showcasing a reduction in assembly defects from 2.59% to 0.24% and an increase in satisfaction rates among device users from 95.52% to 97.61%.
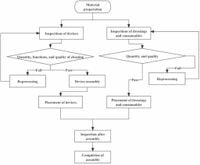
The HACCP system, traditionally utilized in food safety management, was effectively adapted to healthcare context with this study. Researchers established a dedicated HACCP team comprising 16 members to analyze potential hazards during the assembly process concerning reusable devices. They used modern management tools, such as Pareto charts and fishbone diagrams, to identify critical control points and implement preventive measures.
The research revealed that assembly defects often resulted from human errors, outdated processes, and insufficient training amongst personnel. Consequently, the HACCP team's engagement led to systematic approaches in addressing these issues, improving staff training, standardizing procedures, and enhancing traceability systems.
According to the authors, "The implementation of the HACCP system improved the quality of device assembly and significantly reduced the assembly defect rates,” which reflects a substantial advancement towards enhancing healthcare safety.
Notably, the study received ethical approval, adhering to the Declaration of Helsinki, ensuring that all research methods complied with established guidelines. The interventions included splitting job responsibilities among assembly and packaging to streamline operations and reduce the workload of personnel, particularly in high-pressure environments.
By identifying key defects and implementing tailored training programs, the HACCP system equipped staff with the necessary skills to maintain high standards of service and precision in device assembly. User satisfaction correlated strongly with these improvements, illustrating the direct impact of operational quality on clinical outcomes.
Moving forward, the authors advocate for the broader adoption of the HACCP management system within various medical facilities to enhance the quality control of reusable medical devices. They emphasize that integrating such systematic approaches can lead to significant improvements in patient safety and healthcare outcomes.
This study not only highlights the efficiency of HACCP in a previously uncharted area but also suggests a future of rigorous quality management in healthcare, fostering an environment where patient safety is prioritized through effective risk management strategies.