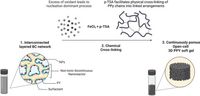
The rising demand for effective, flexible, and lightweight energy storage devices has spurred significant advancements in materials and fabrication techniques, particularly for micro-supercapacitors (MSCs). A recent study led by a team of researchers has unveiled a groundbreaking template-free bicontinuous microemulsion (BME)-based method for fabricating polypyrrole-cobalt oxide (PPy-CoO) electrodes, promising a new era in micro-pseudocapacitors (MPCs).
This study introduces a novel approach that overcomes traditional challenges, such as poor cycling and mechanical stability in conducting polymers. By integrating PPy, known for its excellent electrical properties, with cobalt oxide, notorious for its high charge-storage capacity, the research team crafted highly cross-linked, continuously porous electrodes. The result? An innovative design that not only enhances electrical performance but ensures the flexibility necessary for next-generation smart electronics.
The advantages of this method are evidenced by the impressive performance metrics of the resulting micro-pseudocapacitors. The device boasts an areal capacitance of 30.58 mF cm−2, an energy density of 4.22 µWh cm−2, and a power density of 75.97 µW cm−2 at 0.2 mA cm−2. Additionally, the electrodes retain 106% capacitance under 180° bending, demonstrating remarkable compliance with mechanical stress. Moreover, the device exhibits 83% capacitance retention even after 10,000 cycles in a bent position, a significant milestone for flexible energy storage solutions.
The seamless execution of the BME method fosters a self-assembled, open-cell structure that enhances ion diffusion, ultimately leading to improved electrochemical and mechanical performance. The integration of cobalt oxide into the polymer network not only elevates the charge storage capacity but also guarantees long-term stability, crucial for practical applications in flexible electronics and portable devices.
The findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports. The significance of this research extends to various fields, from renewable energy technologies to the development of wearable electronics. As the demand for efficient and portable energy solutions continues to accelerate, innovations like these pave the way for the next generation of micro-scale energy devices.
Dr. Zhigerbayeva and her team have meticulously demonstrated the efficacy of their approach, with their experiments underscoring the robustness and versatility of the constructed materials. Their research highlights the potential of PPy-CoO micro-pseudocapacitors as a low-cost, highly efficient option for energy storage, addressing a critical need in modern technology.
With the continued exploration in this domain, the researchers aim to expand their investigations into other hybrid conducting polymers, enhancing performance across diverse applications. The developments could not only enhance smart devices but also contribute toward reliable energy solutions that respond to the ever-increasing demand for advanced electronics.
In summary, the innovative fabrication technique detailed in this study represents a significant leap forward in the realm of micro-supercapacitors, solidifying its potential impact on future developments in flexible energy storage systems.