The economic landscape in Germany is facing a stark reality as recent forecasts indicate a grim outlook for both East and West regions. The Halle Institute for Economic Research (IWH) reported that the economy in East Germany shrank by 0.1% in 2024, while the entire German economy contracted by 0.2%. As the nation grapples with geopolitical tensions and new tariffs imposed by the United States, the economic forecast for East Germany remains stagnant for 2025, with only a slight growth of 1.1% anticipated for 2026.
In its Spring Report released in April 2025, the Joint Economic Forecast Project Group underscored that the German economy has been in crisis since late 2023. The report attributes this downturn to the negative impacts of new US tariffs and a high level of political uncertainty, which are expected to dampen economic activity in 2025. While East Germany's exports to the US are less significant compared to its western counterpart, the economic strain is palpable.
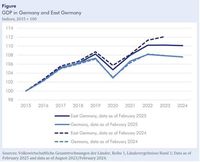
In 2024, the gross domestic product (GDP) in East Germany fell slightly less than in West Germany, which recorded a decrease of 0.3%. Interestingly, production in Berlin saw an increase of 0.8%, but this was offset by a 0.5% decline in the other East German states. The IWH's recent publication of production figures also revealed a downward revision of East Germany's GDP growth over the past few years. Initially reported as 12.1% higher in 2023 compared to 2015, revised calculations now show a mere 10.2% increase.
Such revisions were particularly pronounced in regions like Brandenburg, where growth was adjusted from 11.6% to 4.5%, and in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, which fell from 13.3% to 7.3%. In Saxony-Anhalt, the situation appears even bleaker, with a revision from a 3.3% growth to a slight contraction of 0.1%.
As the economic challenges mount, Oliver Holtemöller, Head of the Department of Macroeconomics at IWH, warns that a decline in the workforce will increasingly burden the East German economy. In 2024, the number of employees subject to social insurance contributions fell by 0.1% in East Germany, contrasting with a 0.4% increase in West Germany. This demographic shift poses significant challenges for the region's economic future.
Looking ahead, the IWH forecasts an unemployment rate of 7.8% for both 2025 and 2026, slightly higher than the 7.5% recorded in 2024. This stagnation in employment reflects broader trends affecting the German economy as a whole, which is grappling with structural issues such as a shortage of skilled workers and increased competition from China.
Meanwhile, the six major think-tanks have revised their growth predictions, now estimating a mere 0.1% growth for Germany in 2025, a significant drop from the 0.8% expansion forecasted just a few months earlier. For 2026, they maintain a projection of 1.3% growth, unchanged from prior estimates. Torsten Schmidt, head of research at the RWI-Leibniz Institute for Economic Research, stated, "The geopolitical tensions and the protectionist trade policy of the USA are exacerbating the already tense economic situation in Germany."
These predictions come on the heels of the French and Italian governments also cutting their growth forecasts, pointing to new trade barriers and warning of potential economic stagnation. The tariffs imposed by the US on aluminum, steel, and vehicle imports are expected to reduce Germany's economic growth by 0.1 percentage points for both 2025 and 2026, according to the think-tanks' calculations. Furthermore, reciprocal tariffs announced by the US could potentially double this impact, although quantifying the exact effects remains challenging.
Adding to Germany's economic woes, the country faces deep-seated structural issues, including stifling bureaucracy and high taxes. The think-tanks emphasized that these challenges cannot be resolved simply by increasing government spending, highlighting the urgent need for reforms to boost potential output.
The German government's latest official forecast, released in January, projected a growth of 0.3% for the year. However, a new forecast is set to be presented on April 24th, which may further adjust these expectations. Friedrich Merz, the chancellor-in-waiting, recently presented a coalition agreement between his center-right CDU/CSU and the leftist SPD, setting the stage for his ascension to power next month.
Merz's coalition is faced with the formidable task of reviving Germany's economy, which has experienced a manufacturing slump and weak demand in key markets for the past two years. As competition from China intensifies, the new government’s approach will be closely scrutinized. Merz has already taken steps to modify Germany's debt regulations, allowing for potentially unlimited government borrowing for defense.
Additionally, he secured parliamentary approval for a €500 billion fund aimed at renovating Germany's aging infrastructure. Economists estimate that this investment could boost growth by 0.5 percentage points over the next year, contingent on an additional €24 billion in government spending. However, some experts criticize the coalition's plans, arguing that they fall short of addressing the pressing need for structural reforms that could yield long-term growth benefits.
Marcel Fratzscher, head of the German Economic Institute for Economic Research (DIW), remarked, "The coalition agreement between the CDU/CSU and SPD is a compromise that largely maintains the status quo." He emphasized that the urgency of the current crisis has not yet been fully recognized by the coalition, raising concerns about their ambitiousness in tackling the economic challenges ahead.
As Germany stands at a crossroads, the coming months will be crucial in determining whether the new government can navigate these turbulent waters and steer the economy toward recovery. With both East and West facing distinct yet interconnected challenges, the path forward will require decisive action and innovative solutions to restore confidence and foster sustainable growth.