Artificial intelligence is redefining the boundaries of music composition. Recent research highlights the innovative use of algorithms to compose national ballads infused with ethnic characteristics, representing not just cultural expression but also technological advancement. The study introduces a sophisticated music composition model combining the Markov chain (MC) and Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network (Bi-RNN) to generate melodies and emotional nuances akin to traditional national ballads.
National ballads hold significant emotional weight and historical significance within Chinese culture. They encapsulate the essence of traditional folk expressions, transcending mere entertainment to reflect the collective memory and sentiments of diverse ethnic communities. Despite their importance, the art of crafting these melodies poses challenges due to the intricacies involved, which modern technology aims to alleviate.
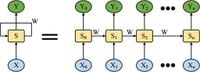
The proposed model utilizes the MC to set the foundational melody structure, leveraging its capacity for statistical analysis of note sequences to forecast musical transitions. Following this initial processing, the Bi-RNN refines the rhythm and emotional expression, employing deep learning techniques to produce compositions echoing the spirit of ethnic music.
The model was validated through experimental assessments, demonstrating its superior abilities compared to traditional manual composition and the MC alone, significantly enhancing the creative output and fidelity to ethnic styles. With the advent of such technology, the research broadens the horizon for music education, providing tools for preserving and innovatively advancing cultural heritage. One must note the rise of AI technology's role in artistic endeavors; it has been increasingly recognized as pivotal for music educators and students alike.
Wu et al. (2019) noted the growing exigency for flexible learning approaches among students, insisting on the incorporation of various educational methods to facilitate music composition. Similarly, Wu and Chen (2021) underlined the value of experiential learning via innovative curricula, connecting it to the course of national music composition.
By integrating contemporary technological advancements, the research potentially overcomes traditional geographical and resource limitations faced during national ballad creation. The methodology hinges on deep learning's capacity to analyze and replicate melodic structures intrinsic to national ballads, thereby reinvigorate the genre through algorithmic innovation.
The constructed model not only provides artistic direction but also contributes to effective educational practices by ensuring accessibility to musical resources, which have long been scarce. Prior AI innovations, as outlined by Min et al. (2022), showcased tangible improvements where machine-generated compositions approached human creativity. Studies like those of Bihani et al. (2023) support the notion of merging AI with artistic expression to yield compositions with enhanced coherence and aesthetic quality.
At the core of the research is the emphasis on using the pentatonic scale traditionally associated with Chinese national ballads. The absence of half-step intervals enriches melodies with flowing dynamics, producing softer, more harmonious expressions. Together with automated learning techniques, the MC operates efficiently to formulate melodies, aligning with the cultural nuances embedded in national ballads.
The experimental setup assessed various compositions drawn from both algorithmic and traditional sources. A collection of thirty national ballads—comprised of ten manually composed pieces, ten generated by the innovative Markov Bi-RNN model, and ten by the MC—serves as the foundation for evaluation based on five key criteria: melody, rhythm, aesthetic feeling, and emotional expression.
Results from these evaluations led to insightful revelations on the comparative effectiveness of AI-generated compositions. Specifically, the Markov Bi-RNN model produced scores of 85.1 for melody, 88.3 for rhythm, and 87.1 for emotional expression. When compared with manually composed counterparts, which achieved scores of 95.7, 93.2, and 89.7 respectively, it is clear there is significant promise—and room for enhancement—within the technological approach.
Relatedly, supplementary assessments using the Lakh MIDI Dataset revealed consistent performance trends indicating the reproducibility and adaptability of the Markov Bi-RNN model across different styles, fortifying its viability within the broader scope of music composition.
While AI models have made commendable strides, the study acknowledges inherent limitations, particularly surrounding emotional expressiveness. The nuanced sentiments often conveyed through traditional composition methods continue to challenge algorithmic interpretations, underscoring the importance of future advancements aimed at incorporating varied stylistic features and addressing user-specific needs much more thoroughly.
To catalyze future research, scholars should pursue innovations to augment the capacities of AI technologies, aiming for compositions with heightened emotional resonance and cultural fidelity. The exploration of how AI can creatively engage with traditional artistic domains not only underlines the intersection of technology and culture but also ensures the vibrant continuation of folkloric heritage against the encroachment of globalization. The practical applications outlined herein signal significant opportunities for integrating artificial intelligence within music education and culture, promising both preservation and evolution of ethnic musical forms.
Overall, this study highlights the immense potential embedded within AI-driven methodologies for redefining traditional music composition practices. The era of synergizing artificial intelligence with ethnic creativity has arrived, laying the groundwork for brighter, harmonized futures where technological advancements and cultural roots can coexist harmoniously.