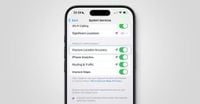
On April 2, 2025, Apple rolled out its latest software update, iOS 18.4, introducing a range of exciting features that have caught the attention of users worldwide. Among the standout additions are Priority Notifications, new emoji options, and the innovative Sketch in Image Playgrounds. However, the update also includes a less-publicized but significant change: a new setting in Location Services called ‘Improve Location Accuracy.’
This new feature, which was reportedly enabled by default for some users, can be found by navigating to Settings -> Privacy & Security -> Location Services -> System Services and scrolling down to the ‘Product Improvement’ section. This toggle joins existing settings such as ‘iPhone Analytics,’ ‘Routing & Traffic,’ and ‘Improve Maps.’
According to Apple’s documentation, the ‘Improve Location Accuracy’ setting allows the iPhone to periodically send the geo-tagged locations of nearby Wi-Fi hotspots and mobile phone masts in an anonymous and encrypted form to Apple. This data is intended to enhance the crowd-sourced database of Wi-Fi and mobile phone mast locations, which is crucial for improving the accuracy of the device's location services.
While turning off ‘Improve Location Accuracy’ doesn’t prevent users from benefiting from the crowd-sourced database, it does provide a way for users to opt out of contributing their data to the assisted GPS system. Apple reassures users that the data sent is anonymized and encrypted, alleviating potential privacy concerns.
In a related technological trend, ChatGPT has recently seen a surge in new users, driven by its latest image generator and the viral Ghibli-style image craze. However, this rise in popularity has also raised alarms among data privacy experts regarding the uploading of private and personal photos to AI platforms.
ChatGPT has issued warnings about sharing sensitive data, emphasizing that while it does not store or use uploaded images beyond the immediate prompt, users should still exercise caution. The AI suggested that if privacy is a concern, individuals consider using offline tools or apps specifically designed for secure image processing.
Similarly, Elon Musk's Grok 3 has cautioned users against uploading sensitive photos, noting that xAI, the company behind Grok, utilizes data from its subsidiary X (formerly Twitter) to enhance its AI tools unless users opt out. Grok's warnings highlight the potential vulnerabilities in data privacy, urging users to think twice before sharing images that could contain sensitive information.
As the conversation around data privacy continues, many are left wondering about the implications of using VPNs, or virtual private networks. While VPNs are popular for enhancing online privacy by hiding internet activity, it’s crucial to understand their limitations.
Experts agree that no privacy tool, including VPNs, can guarantee 100 percent privacy online. Privacy refers to the ability to hide activities from third parties, such as ISPs or hackers, while anonymity means leaving no trace of one’s online presence. Achieving complete anonymity is nearly impossible in a world filled with trackers and data collection.
Despite these limitations, VPNs remain valuable tools for maintaining a higher level of privacy. By encrypting data and masking IP addresses, VPNs can help users evade prying eyes. However, users should be cautious; while a VPN can obscure browsing activity from ISPs, it cannot hide data provided to websites or the total bandwidth used.
For instance, while a user may browse anonymously, once they log into a website, their activity can still be tracked. This underscores the importance of being mindful of what information is shared online, regardless of VPN usage.
On April 2, 2025, Cisco released its 2025 Data Privacy Benchmark Study, revealing significant insights into privacy trends and their implications for businesses. The study found that 86% of respondents support privacy legislation, recognizing its positive impact on business operations. In fact, 96% of organizations reported that privacy investments yield returns exceeding their costs.
As familiarity with AI rises—63% of respondents indicated they are very familiar with Generative AI—concerns about unintended risks remain prevalent. Notably, 64% of those surveyed worry about inadvertently sharing sensitive information publicly or with competitors when using GenAI tools. This gap highlights the need for robust governance measures to safeguard against data misuse.
Furthermore, 90% of organizations view local data storage as inherently safer, while 91% trust global providers for better data protection. This duality illustrates the complex landscape of data privacy, where local storage is perceived as safer despite the operational costs associated with it.
Dev Stahlkopf, Cisco's Chief Legal Officer, emphasized the importance of privacy and data governance as foundational elements for Responsible AI. He stated, "Privacy and proper data governance are foundational to Responsible AI," underscoring the need for organizations to establish solid data privacy frameworks as they prepare for AI integration.
The study also revealed that 99% of respondents anticipate reallocating resources from privacy budgets to AI initiatives in the future, indicating a shift in focus as companies aim to safely deploy AI technologies. Cisco plans to continue monitoring this trend, recognizing the intertwined roles of privacy and AI governance in fostering safe and reliable AI systems.
In conclusion, as technology evolves and the digital landscape becomes increasingly complex, the importance of data privacy cannot be overstated. Whether it’s through new software updates like iOS 18.4, the cautious use of AI platforms, or the implementation of VPNs, individuals and organizations alike must prioritize privacy to navigate the challenges of the modern digital world.