The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) optimization algorithms into higher education management and personalized teaching is transforming traditional educational practices. Recent research highlights the potential and effectiveness of these technologies in enhancing student outcomes and streamlining administrative processes. An empirical study conducted over an academic semester demonstrates that AI-driven personalized teaching significantly improves student learning outcomes, engagement, and satisfaction when compared to conventional educational methods.
The advancements in AI have sparked interest in their application within education, particularly for optimizing resource allocation and tailoring personalized learning experiences. With higher education institutions facing increasing demands for quality education and efficient management solutions, AI optimization algorithms offer promising pathways for addressing these challenges.
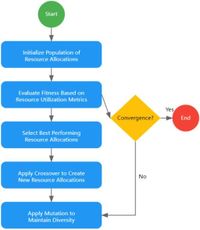
This research reveals that AI can effectively solve complex educational management issues by analyzing large datasets and automating administrative tasks. For example, AI can optimize course scheduling, faculty assignments, and classroom utilization, enabling institutions to maximize their resources. These algorithms employ methods like evolutionary algorithms, swarm intelligence, and physics-based approaches to find optimal solutions to educational challenges.
One key finding of the study was the substantial improvement in learning outcomes among students who engaged with AI-based personalized teaching methods. The traditional learning model, which often adopts a one-size-fits-all approach, is increasingly recognized as insufficient to meet the diverse needs of modern learners. Personalized teaching, on the other hand, tailors learning experiences to individual students' unique needs, preferences, and abilities, resulting in improved academic performance and greater student satisfaction.
The research involved 120 students and 15 educators from a notable higher education institution. Participants were divided into control and treatment groups. The treatment group utilized AI optimization for personalized learning and resource management, while the control group followed traditional educational approaches.
Data analysis revealed that the AI-driven personalized teaching approach led to an increase in average student performance scores from 74.2 to 87.1, with engagement levels rising proportionately and satisfaction scores reflecting similarly positive trends.
However, the study did not shy away from acknowledging the challenges faced by higher education institutions in implementing these AI solutions. Issues identified included data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, and the resistance of faculty and staff to change. Ensuring that AI algorithms are transparent, accountable, and aligned with institutional goals is crucial for effective implementation.
The findings underscore the importance of continuous development of adaptive algorithms and caution against the misallocation of resources due to biases inherent in AI technologies. Future research directions emphasize the need for ethical frameworks governing AI integration into educational practices.
As educational institutions navigate the complexities of adopting artificial intelligence, the embrace of AI optimization can lead to profound improvements in both teaching quality and administrative efficiency. The ongoing evolution of personalized teaching approaches represents a critical shift toward meeting the needs of diverse learners in an increasingly complex educational landscape.