A Newly Developed Frequency Agile Antenna Enhances 5G Connectivity
Researchers unveil a dual-band to wideband MIMO antenna that optimizes performance for 5G New Radio applications.
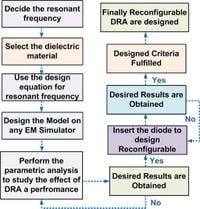
As the demand for faster and more reliable wireless communication continues to rise, researchers have made a significant stride in antenna technology with the introduction of a groundbreaking dual-band to wideband Frequency Agile (FA) rectangular dielectric resonator (DR) hybrid MIMO antenna. Designed specifically for 5G New Radio (NR) applications, this innovative antenna promises improved performance while addressing the challenges related to multipath fading that can interfere with signal clarity.
The innovative antenna is constructed using Al2O3 ceramic material, known for its high dielectric constant (εr = 9.8), which enhances performance. The key feature of this antenna is its adaptability, achieved through the use of PIN Diode switches. When the PIN Diode is in an “ON” state, the antenna operates in dual-band mode, exploiting the TE111 mode. Conversely, switching the PIN Diode to an “OFF” state permits a broader frequency range by exciting both the TE111 and TE211 modes.
In practical terms, the antenna exhibits impressive performance metrics with isolation reaching 20 dB and a gain of 4.3 dBi, demonstrating its strength in maintaining signal integrity. Furthermore, it boasts a remarkable tuning range of 49.36, enhancing its versatility. These characteristics make it suitable for the diverse operational requirements of emerging 5G technologies.
Compared to existing designs, the new MIMO antenna stands out due to its efficient use of space and materials. As highlighted in the research, traditional microstrip patch antennas, although popular, often face challenges related to low radiation efficiency. On the other hand, the dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) proves to be a viable alternative, offering a wider bandwidth and higher radiation efficiency.
Researchers conducted comparative studies, finding limited existing literature on dual or triple-band DRA-based MIMO antennas, particularly in lower frequency ranges. This novel design enhances multi-band LTE MIMO operations and is expected to significantly improve user experience in high-density locations, supporting multiple connections with higher throughput.
As technology advances, researchers also leveraged machine learning (ML) algorithms to further optimize antenna design. Employing various ML techniques, the study indicated that the Random Forest (RF) algorithm achieved remarkable accuracy, surpassing 99% in predicting S-parameters. This convergence of antenna technology and machine learning promises to streamline design processes and improvements.
The researchers highlighted that optimizing configurations based on dielectric constants is crucial, as varying dielectric constants of the DR significantly impact bandwidth and impedance matching. The study reported the optimum dimensions for the dielectric resonator to be 16 mm in length and width, with a height of 8 mm.
The antenna's versatility is well illustrated by its performance metrics under various configurations, achieving dual-band characteristics in the “ON-ON” state while achieving wideband characteristics when the states are switched to “OFF-OFF.” Notably, the antenna supports frequency ranges of 2.21 to 2.9 GHz and 4.49 to 5.64 GHz in its dual-band operation, and a wideband response spanning 2.9 to 5.65 GHz among other configurations.
In evaluating the MIMO performance parameters, researchers found the envelope correlation coefficient (ECC) at 0.05, diversity gain (DG) around 10 dB, and total active reflection coefficient (TARC) values at 0 dB. These metrics confirm its efficacy as a MIMO device tailored for innovative 5G applications.
The advancements presented by this dual-band to wideband Frequency Agile DR-based antenna mark a significant step towards fulfilling the growing demand for high-speed wireless connectivity. Researchers expect its widespread adoption to play a crucial role in the future development of efficient and high-capacity wireless communication systems.
This work was recently published on March 20, 2025, in the journal Scientific Reports by a team of researchers led by Jayant Kumar Rai and Ajay Kumar Dwivedi, contributing substantially to the ongoing discourse surrounding antenna technology in the wireless communication arena.